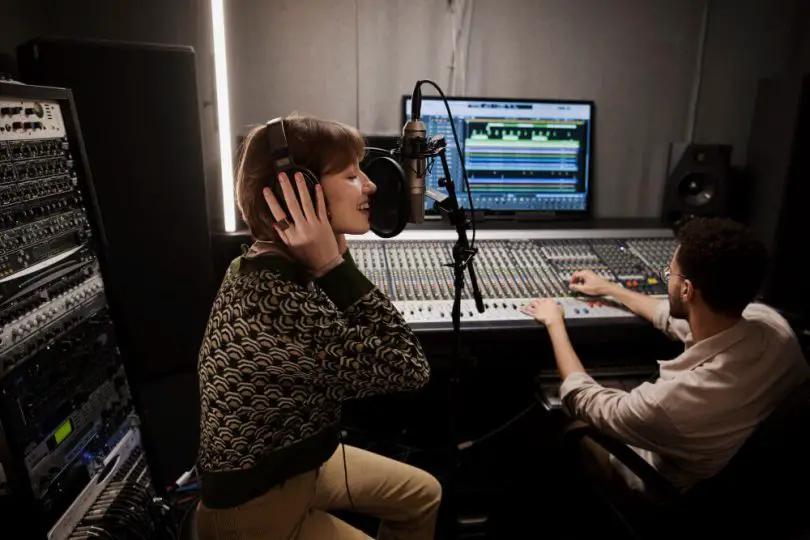
Have you ever listened to a recording of your voice and thought, “That’s not what I sound like!”? You’re not alone. Many people are surprised by how different their voice sounds when it’s recorded and played back. But why does this happen?
The main reason why your voice sounds different on a recording is because of the way sound behaves in different environments.
When you speak, your voice travels through the air and is heard by the person you’re speaking to. But when you listen to a recording of your voice, the sound is passing through the air and through the speakers or headphones before it reaches your ears. This can change the way your voice sounds, making it seem higher or lower than you’re used to.
Another reason why your recorded voice might sound different is because of the way sound waves travel through your body.
When you speak, you hear your voice in two different ways: through the air and through the vibrations in your skull. But when you listen to a recording of your voice, the bone-conducted pathway that you consider part of your “normal” voice is eliminated, and you hear only the air-conducted component in the recording. This can make your voice sound thinner or less resonant than you’re used to.
The Science Behind Voice Recording
How Sound Waves Work
Sound is a type of energy that travels through the air in the form of waves. When we speak, our vocal cords vibrate, creating sound waves that travel through the air and into our ears.
These sound waves are made up of compressions and rarefactions, which are areas of high and low pressure. The frequency of the sound waves determines the pitch of the sound, while the amplitude determines the volume.
When we hear our own voice, we are actually hearing two different things: the sound waves that travel through the air and the sound waves that travel through our bones.
The sound waves that travel through our bones are lower in frequency and higher in amplitude, which gives our voice a deeper, richer tone.
When we hear a recording of our voice, we are only hearing the sound waves that travel through the air, which can make our voice sound higher and thinner than we are used to.
How Microphones Work
A microphone is a device that converts sound waves into an electrical signal that can be recorded or amplified. There are several different types of microphones, but they all work on the same basic principle: a diaphragm vibrates in response to sound waves, which causes a coil of wire to move back and forth in a magnetic field. This movement generates an electrical signal that corresponds to the sound waves.
When we speak into a microphone, the sound waves from our voice cause the diaphragm to vibrate, which generates an electrical signal that can be recorded or amplified.
However, not all microphones are created equal. Different types of microphones have different frequency responses, which can affect the way our voice sounds on a recording.
For example, some microphones are designed to emphasize the low frequencies in our voice, while others are designed to capture a more natural, balanced sound.
Factors That Affect Voice Recording
Acoustics of the Room
The acoustics of the room in which you are recording can have a significant impact on the sound of your voice. If you are recording in a room with hard surfaces, such as tiles or concrete, the sound waves reflecting off the walls can create echoes and reverberations, which can distort the sound of your voice.
In contrast, recording in a room with soft surfaces, such as carpeting or curtains, can absorb sound waves and create a more natural, balanced sound.
Distance from the Microphone
The distance between your mouth and the microphone can also affect the sound of your voice on a recording. If you are too close to the microphone, the sound of your voice can become distorted, with pops and hisses caused by the air from your breath hitting the microphone.
On the other hand, if you are too far away from the microphone, the sound of your voice can become muffled and indistinct. Finding the right distance from the microphone is essential for achieving a clear, balanced recording of your voice.
Microphone Type
The type of microphone you use can also have a significant impact on the sound of your voice on a recording. Different microphones are designed to capture different aspects of sound, and can result in a range of different tones.
For example, a dynamic microphone is commonly used for live performances and can produce a warm, natural sound, while a condenser microphone is often used in studio recordings and can produce a more detailed, precise sound. Choosing the right microphone for your recording needs is crucial for achieving the desired sound quality.
Why Your Voice Sounds Different on a Recording
Hearing Yourself vs. Hearing a Recording
One reason why your voice sounds different on a recording is due to the way you hear yourself when you speak versus how you hear yourself on a recording. When you speak, sound waves travel through the air and reach your ears through external air conduction.
However, when you listen to a recording of your voice, the sound waves are transmitted through the air and then through the microphone, which can alter the sound of your voice.
Additionally, when you speak, your vocal cords vibrate and create sound waves that travel through your skull to your inner ear, which is called internal bone conduction. This internal conduction can also affect the way you perceive your voice.
Perception of Pitch and Tone
Another reason why your voice may sound different on a recording is due to the perception of pitch and tone. When you listen to a recording of your voice, you may notice that your voice sounds higher or lower than you expected.
This is because the pitch of your voice can be affected by the acoustics of the room, the distance between you and the microphone, and the quality of the recording equipment.
Similarly, the tone of your voice can also be affected by the recording equipment. For example, a microphone may pick up more of the lower frequencies in your voice, which can make your voice sound deeper or more resonant than it does in person.
Psychological Factors
Finally, psychological factors can also play a role in why your voice sounds different on a recording. When you listen to a recording of your voice, you may be more critical of your own voice and notice flaws or imperfections that you wouldn’t notice when speaking in person.
This can lead to a perception that your voice sounds different on a recording, even if the recording is an accurate representation of your voice.
Additionally, some people may feel self-conscious or nervous when speaking into a microphone, which can affect the way they speak and the sound of their voice on a recording.
Tips for Improving Your Voice Recording
Adjusting Your Recording Setup
When it comes to recording your voice, the setup you use can make a big difference in how you sound. Here are some tips for adjusting your setup to improve your recordings:
- Choose a quiet location with minimal background noise.
- Use a pop filter to reduce plosives and sibilance.
- Position your microphone at the correct distance and angle from your mouth.
- Experiment with different microphone types to find the one that works best for your voice.
- Use headphones to monitor your recording and ensure that you’re getting a clean signal.
Practicing Speaking on a Microphone
Even with the best recording setup, your voice can still sound different on a recording if you’re not used to speaking on a microphone. Here are some tips for practicing and improving your microphone technique:
- Practice speaking at a consistent volume and distance from the microphone.
- Try to avoid speaking directly into the microphone, as this can cause distortion or clipping.
- Experiment with different speaking techniques to find the one that works best for your voice.
- Record yourself speaking and listen back to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
- Consider taking a voice-over class or working with a vocal coach to improve your technique.
By adjusting your recording setup and practicing speaking on a microphone, you can improve the quality and consistency of your voice recordings. Keep in mind that it may take some time and experimentation to find the setup and techniques that work best for your voice.