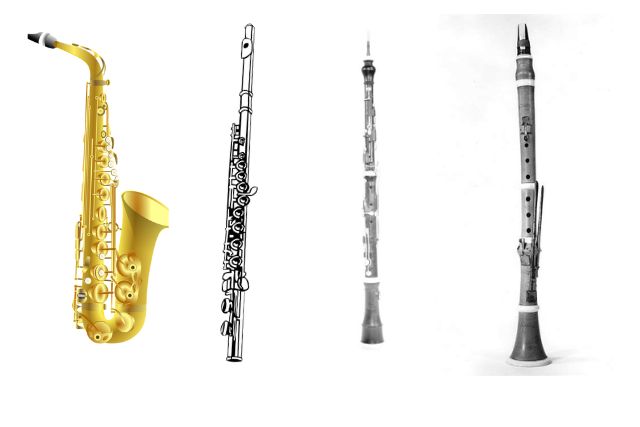
Woodwind instruments are a group of musical instruments that generate sound by blowing air into them. They are frequently used in orchestras, bands, and other musical groups. The woodwind family comprises a range of instruments, including the flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two primary categories of woodwind instruments: flutes and reed instruments.
Flutes are played by blowing air across a hole in the instrument, while reed instruments are played by blowing air through a reed. The sound produced by woodwind instruments is created by the vibration of the air column inside the instrument.
Woodwind instruments have a long history and have been used in music for centuries. They are versatile instruments that can produce a wide range of sounds, from soft and delicate to loud and powerful. Whether you are a professional musician or a beginner, learning to play a woodwind instrument can be a rewarding experience that allows you to express yourself through music.
History of Woodwind Instruments
Woodwind instruments have been an integral part of music for centuries. The earliest known woodwind instruments date back to ancient civilizations, such as Egypt and Greece.
These early instruments were typically made from hollowed-out reeds or animal horns and were used for religious ceremonies and other important events.
Early Woodwind Instruments
During the Middle Ages, woodwind instruments began to evolve and become more complex. The recorder, which is still used today, was developed during this time. Other early woodwind instruments included the shawm, which was used in military bands, and the crumhorn, which was popular in Renaissance music.
As music continued to evolve, so did woodwind instruments. In the 18th century, the clarinet was invented, followed by the bassoon and the oboe. These instruments became increasingly popular in orchestras and chamber music groups.
Development of Modern Woodwind Instruments
During the 19th and 20th centuries, woodwind instruments continued to evolve and improve. The saxophone, which was invented in the mid-1800s, became a popular instrument in jazz music.
The flute also underwent significant changes during this time, with the development of the Boehm system, which allowed for more complex fingerings and a wider range of notes.
Nowadays, woodwind instruments are crafted using various materials, such as wood, metal, and plastic. They are utilized in a diverse range of musical genres, including classical, jazz, and pop.
Types of Woodwind Instruments
Woodwind instruments generate sound by blowing air into them and are categorized as a family of musical instruments.
They are an essential part of any orchestra and can also be played solo or in smaller ensembles. Woodwind instruments can be divided into two main categories: flutes and reed instruments.
Within these categories, there are several types of woodwind instruments that produce different sounds and are used in different musical contexts.
Flutes
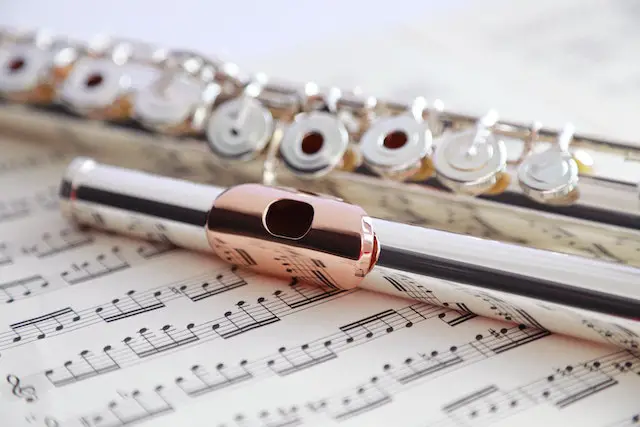

Flutes are a type of woodwind instrument that produce sound by blowing air across a hole in the instrument. They are typically made of metal or wood and come in a variety of sizes. Here are a few popular types of flutes:
- Western concert flute
- Piccolo
- Alto flute
- Bass flute
- Irish flute
- Native American flute
Flutes are known for their clear, bright sound and are often used in classical music, folk music, and jazz.
Clarinets

Clarinets are a type of reed instrument that produce sound by blowing air through a single reed attached to the mouthpiece. They are typically made of wood or plastic and come in a variety of sizes. Some common types of clarinets include:
- B-flat clarinet
- A clarinet
- Bass clarinet
- Contrabass clarinet
Clarinets are known for their warm, mellow sound and are often used in classical music, jazz, and marching bands.
Saxophones

Saxophones are a type of reed instrument that produce sound by blowing air through a single reed attached to the mouthpiece. They are typically made of brass and come in a variety of sizes. The following are some popular types of saxophones:
- Soprano saxophone
- Alto saxophone
- Tenor saxophone
- Baritone saxophone
- Bass saxophone
Saxophones are known for their rich, expressive sound and are often used in jazz, blues, and rock music.
Oboes

Oboes are a type of reed instrument that produce sound by blowing air through a double reed attached to the mouthpiece. They are typically made of wood and come in a variety of sizes. Some common types of oboes include:
- Oboe
- English horn
- Piccolo oboe
Oboes are known for their distinctive, nasal sound and are often used in classical music and film scores.
Bassoons

Bassoons are a type of reed instrument that produce sound by blowing air through a double reed attached to the mouthpiece. They are typically made of wood and come in a variety of sizes. Some common types of bassoons include:
- Bassoon
- Contrabassoon
Bassoons are known for their deep, rich sound and are often used in classical music and film scores.
How Woodwind Instruments Work
Woodwind instruments are a group of musical instruments that generate sound by blowing air into them. The vibration of the air column inside the instrument produces the sound.
There are three main components that contribute to the production of sound in woodwind instruments: the air column, the reed or mouthpiece, and the key system.
Air Column and Vibrations
The air column is the hollow tube inside the instrument that the air travels through. When the musician blows air into the instrument, the air column vibrates and produces sound.
The pitch of the sound is determined by the length of the air column. The musician can create various notes by altering the length of the air column.
Reeds and Mouthpieces
Reed instruments, such as clarinets and saxophones, use a thin piece of cane or synthetic material called a reed to produce sound. The reed vibrates against the mouthpiece, which is a small piece of curved metal or plastic that the musician blows into. The shape and size of the mouthpiece affect the sound produced by the instrument.
Flutes and some other woodwind instruments do not use reeds. Instead, they have a mouthpiece that directs the air stream against a sharp edge, creating a vibration that produces sound.
Key Systems
Woodwind instruments have a complex system of keys and finger holes that the musician uses to change the length of the air column and produce different notes.
The keys and holes are typically made of metal and are arranged in a specific pattern to produce the desired notes. The key system allows the musician to play a wide range of notes with only a few finger positions.
By opening and closing different keys and holes, the musician can produce different notes and create a variety of musical effects.
To sum up, woodwind instruments generate sound by blowing air into a hollow tube, causing it to vibrate and produce sound.
The sound is influenced by the reed or mouthpiece and the key system, which allows the musician to produce different notes and create a variety of musical effects.
Playing Techniques for Woodwind Instruments
Embouchure and Breath Control
When playing a woodwind instrument, the embouchure is the position of the mouth and lips around the mouthpiece. A good embouchure is essential for producing a clear and consistent sound. The player should form their lips into a firm, but flexible, seal around the mouthpiece.
The embouchure should be centered on the lips and be relaxed. The performer should avoid biting down on the mouthpiece, as it will create tension and affect the sound. Breath control is also crucial when playing a woodwind instrument.
The player should take deep breaths from the diaphragm and use the air to create a steady stream of sound. The performer should avoid shallow breathing, as it will cause the sound to break up or become weak.
Articulation and Tonguing
Articulation refers to the way in which the notes are separated and connected. Tonguing is the technique used to articulate notes.
The player should use the tongue to create a short, crisp sound at the beginning of each note. The tongue should strike the reed or mouthpiece quickly and lightly, and then release the note with a smooth, steady stream of air.
Fingerings and Trills
Fingerings refer to the placement of the fingers on the instrument to create different notes. Each instrument has its own set of fingerings, and the player should learn them thoroughly to produce accurate notes.
Trills are a technique used to create a rapid alternation between two notes. The player should use a combination of finger movements and breath control to create a smooth and even trill.
In summary, playing a woodwind instrument requires a combination of embouchure, breath control, articulation, tonguing, fingerings, and trills. A player must master these techniques to produce a clear and consistent sound.
Choosing and Caring for Woodwind Instruments
Selecting the Right Instrument
When selecting a woodwind instrument, it is important to consider the player’s skill level, musical goals, and personal preferences.
Beginners may want to start with a more common instrument such as the flute, clarinet, or alto saxophone, while more advanced players may prefer the unique sound of the oboe or bassoon.
It is also important to consider the cost of the instrument and the availability of accessories such as reeds, mouthpieces, and cleaning supplies.
Researching different brands and models can help players make an informed decision and find an instrument that fits their needs and budget.
Maintaining and Repairing Woodwind Instruments
Proper maintenance and care can help prolong the life of a woodwind instrument and ensure it sounds its best. Regular cleaning, oiling, and replacing worn parts such as pads and springs can help prevent damage and keep the instrument in top condition.
Players should also be aware of common issues such as leaks, cracks, and damage to the mouthpiece or reed. Seeking the help of a professional repair technician can help address these issues and ensure the instrument is functioning properly.
In addition to regular maintenance, players should also store their instruments in a safe and dry location, avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures or humidity, and handle them with care to prevent accidental damage.
Overall, choosing and caring for a woodwind instrument requires careful consideration and attention to detail. With the right instrument and proper care, players can enjoy the unique sound and versatility of woodwind instruments for years to come.