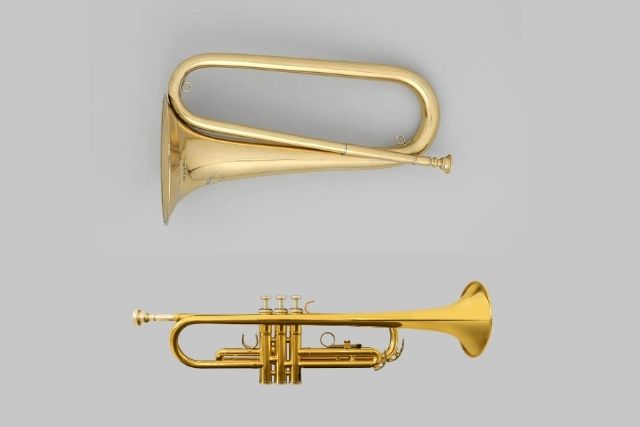
Are you a brass player trying to decide between the Bulge vs Trumpet? While these instruments share many similarities, they also have distinct differences that can impact your playing style and preferences. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between the bugle vs trumpet, from their history and construction to their sound and range.
We’ll also provide tips on how to choose the right instrument for your needs and goals as a musician. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the bugle vs trumpet debate and be able to make an informed decision about which instrument is the best fit for you.
So, if you’re ready to explore the world of brass instruments and discover the differences between the bugle vs trumpet, let’s dive in and get started!
Understanding the Trumpet
History of the Trumpet
The trumpet is a brass musical instrument with a long and rich history. Ancient trumpets were used for signaling in battle and hunting, but the modern trumpet as we know it today evolved from the natural trumpet in the early 17th century. The natural trumpet was a long, straight tube with no valves, which limited the number of notes that could be played.
In the late 18th century, valves were added, allowing the player to produce a wider range of notes and enabling the trumpet to become a more versatile instrument.
Construction and Appearance
The trumpet is a cylindrical brass instrument with a flared bell and a mouthpiece at the opposite end. It typically has three piston valves that are used to change the length of the tubing and produce different notes.
The tuning slide is used to adjust the pitch of the instrument. Trumpets come in various sizes, with the most common being the C trumpet, but other types include the piccolo trumpet, bass trumpet, pocket trumpet, and slide trumpet.
Sound and Pitch
The trumpet produces a bright, piercing sound that is well-suited for fanfares, military music, and jazz. It has a range of approximately three octaves and can play notes in both the treble and bass clefs. The pitch of the trumpet is determined by the length of the tubing and can be adjusted by using the valves or tuning slide.
Versatility and Use in Music
The trumpet is a flexible instrument that is utilized in a broad spectrum of music genres, such as classical, jazz, and pop. It is often used as a solo instrument, but it is also an important part of orchestras, bands, and ensembles.
The trumpet is particularly well-suited for playing melodies and solos, but it can also be used to provide rhythmic support and harmony.
Technique and Skill Required
Playing the trumpet requires a combination of technical skill and musicality. The player must have a good embouchure (the way in which the lips and mouth are used to produce sound), breath control, and finger dexterity. The player must also be able to read music and understand music theory.
With practice and dedication, anyone can learn to play the trumpet at a basic level, but mastering the instrument requires years of study and performance experience.
Exploring the Bugle
Bugle’s Origin
The bugle is a brass musical instrument that has been used for centuries in various forms. Its origin can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome.
The bugle was used in military contexts to signal troops and communicate orders. It was also used in hunting and sporting events. The modern bugle is a simplified version of the trumpet, which was developed in the 19th century.
Design and Look
The bugle is a long, slender instrument made of brass. It has no valves, which means that the player must rely on their lips and breath control to produce different notes.
The mouthpiece of the bugle is smaller than that of the trumpet, and the instrument is usually shorter. The bugle has a distinctive conical shape and a flared bell. It is usually played in a standing position.
Tonal Quality and Range
The bugle has a unique sound that is clear and bright. It has a limited range, typically spanning about six notes. The bugle’s range and tonal quality make it ideal for playing simple melodies and military calls.
The bugle is not as versatile as other brass instruments like the trumpet or trombone, which can play a wider range of notes and styles.
Purpose and Application
The bugle is primarily used in military contexts to signal troops and communicate orders. It is also used in scouting and other youth organizations to teach discipline and teamwork.
The bugle’s distinctive sound has made it a popular instrument for playing Taps, a bugle call that is traditionally played at military funerals.
Learning and Playing the Bugle
Learning to play the bugle requires discipline and practice. The player must develop strong breath control and lip strength to produce clear notes.
The bugle is a challenging instrument to play, but it can be rewarding for those who master it. The bugle is an excellent choice for beginners who want to learn a brass instrument but are intimidated by the complexity of the trumpet or trombone.
Comparison Between Trumpet and Bugle
Physical Differences
The most noticeable physical difference between a trumpet and a bugle is the number of valves. A trumpet typically has three valves, while a bugle has no valves.
The trumpet has a lead pipe that connects to the mouthpiece, while the bugle has a wider mouthpiece and an S-shaped conical tube. The trumpet has a flared bell, while the bugle has a straight, narrow bell.
Sound and Octave Comparison
The trumpet and bugle produce different sounds due to their construction. The trumpet has a wider range of notes and can play in a higher register than a bugle. The bugle has a limited range of notes and is typically used to play simple melodies.
The trumpet has a more vibrant and adaptable sound and is employed in an array of music genres, such as classical, jazz, and pop music. The bugle is primarily used in military bands and Boy Scouts.
Usage in Different Music Genres
The trumpet is a widely used instrument in jazz ensembles, orchestras, and brass bands. It is used to play solos and lead the trumpet group. The bugle is primarily used in military bands to play signals and calls.
Learning Curve
The trumpet is a difficult instrument to learn due to its complex technique and the need for precise pitch control. The bugle is easier to play since it has no valves, but it still requires skill to produce a good sound. Both instruments require proper embouchure and air flow to produce a clear tone.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both the bugle and the trumpet are excellent instruments that have their own unique qualities. The bugle is a simple instrument that is easy to learn and play, making it a great choice for beginners. It is also a popular choice for military ceremonies and other formal events due to its clear and powerful sound.
On the other hand, the trumpet is a more complex instrument that requires more skill and practice to play effectively. Its adaptability and diversity render it a favored selection for an extensive array of musical genres, such as jazz, classical, and pop music.
Ultimately, the choice between the bugle and the trumpet comes down to personal preference and the specific needs of the musician. Those looking for a simple and powerful instrument for formal occasions may prefer the bugle, while those interested in exploring a wider range of musical styles may prefer the trumpet.
Regardless of which instrument is chosen, both the bugle and the trumpet are sure to provide years of enjoyment and musical fulfillment for those who take the time to learn and master them.