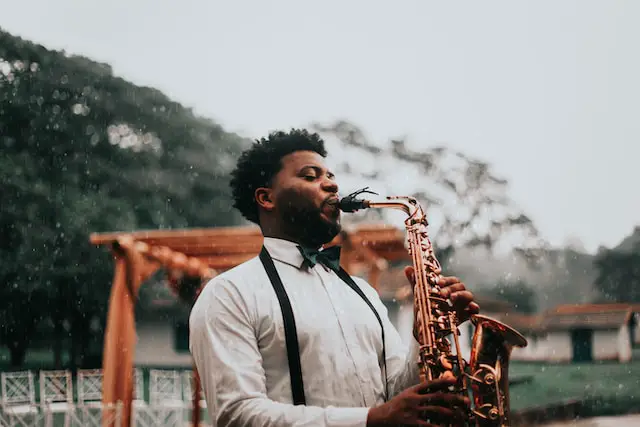
When it comes to musical instruments, the saxophone holds a special place in the hearts of many. Its smooth and soulful sound has made it a favorite in jazz, classical, and contemporary music. But have you ever wondered, is a saxophone a woodwind?
In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of the saxophone, explore its historical context, understand its mechanics of sound production, discuss the different types of saxophones, and highlight some famous saxophonists who have left an indelible mark on the world of music.
Historical Context
To truly appreciate the saxophone and its classification as a woodwind instrument, it’s important to understand its historical context.
The saxophone was invented by Adolphe Sax, a Belgian instrument maker, in the early 1840s. Sax was seeking to create an instrument that combined the best qualities of woodwind and brass instruments. His vision gave birth to the saxophone, which became known for its versatility and unique sound.
Sax’s invention gained popularity and found its way into military bands and orchestras. The instrument’s ability to project a powerful sound, along with its wide range and expressive capabilities, made it a valuable addition to various musical ensembles.
Over the years, the saxophone continued to evolve, with modifications and improvements being made to its design and key mechanisms.
Mechanics of Sound Production
To understand whether a saxophone is truly a woodwind instrument, we need to explore the mechanics of sound production. Like other woodwind instruments, such as the flute and clarinet, the saxophone produces sound through the vibration of a reed.
The reed, which is attached to the mouthpiece, is set into motion when the player blows air into the instrument.
As the air passes through the reed, it vibrates, creating sound waves that travel through the saxophone’s body. The sound is then shaped and amplified by the instrument’s conical shape, keys, and other components.
This mechanism of sound production aligns the saxophone with other woodwind instruments, emphasizing its classification within the woodwind family.
Types of Saxophones
Saxophones come in various sizes and pitch ranges, each with its own unique characteristics and sound. Here are the most common types of saxophones:
- Soprano Saxophone: The smallest member of the saxophone family, the soprano saxophone has a high pitch and a bright, piercing sound. It is often associated with classical and jazz music.
- Alto Saxophone: The alto saxophone is the most commonly played saxophone and is a popular choice for beginners. It has a medium pitch and a rich, expressive tone.
- Tenor Saxophone: The tenor saxophone has a lower pitch than the alto saxophone and is often favored in jazz and rock music. It has a warm and mellow sound that can be both powerful and lyrical.
- Baritone Saxophone: The baritone saxophone is the largest and lowest-pitched saxophone. It produces a deep and resonant sound that provides a strong foundation in many musical ensembles.
- Other Saxophones: In addition to the four main types mentioned above, there are also less common saxophones such as the sopranino saxophone (higher than the soprano) and the bass saxophone (lower than the baritone). These saxophones are less frequently used but add unique tonal possibilities to compositions.
Famous Saxophonists
Throughout history, numerous saxophonists have elevated the saxophone to great heights and showcased its incredible versatility. Let’s take a look at some of the most influential and celebrated saxophonists:
- Charlie Parker: Known as “Bird,” Charlie Parker is considered one of the most influential figures in jazz history. His virtuosic improvisations on the alto saxophone revolutionized the genre and set new standards for technical proficiency.
- John Coltrane: Renowned for his unparalleled improvisational skills and spiritual approach to music, John Coltrane expanded the boundaries of jazz on the tenor saxophone. His innovative playing style continues to inspire saxophonists to this day.
- Stan Getz: Often associated with the cool jazz movement, Stan Getz was a master of the tenor saxophone. His warm and lyrical sound captivated audiences worldwide, particularly with his iconic recording of “The Girl from Ipanema.”
- Lisa Simpson: Although a fictional character, Lisa Simpson from the animated TV show “The Simpsons” has brought attention to the saxophone and inspired many young musicians to pick up the instrument. Lisa’s passion for jazz and her saxophone solos have made her an iconic saxophonist in popular culture.
These are just a few examples of the countless saxophonists who have made significant contributions to the saxophone’s prominence in the music world.
Their artistry and dedication have helped solidify the saxophone’s status as a cherished member of the woodwind family.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the saxophone is indeed a woodwind instrument. Its historical context, mechanics of sound production, and classification within the woodwind family all confirm this classification.
Whether you’re drawn to the soaring melodies of a soprano saxophone or the deep resonance of a baritone saxophone, the saxophone’s unique timbre and expressive capabilities continue to captivate audiences around the globe.
So next time you listen to the mesmerizing sounds of a saxophone, you can appreciate its woodwind heritage and the extraordinary musicians who bring it to life.